CIVIL ENGINEERING
Civil engineering is a professional engineering discipline that deals with the
Design
Construction &
Maintenance
of the physical and naturally built environment, including Public works such as:
Roads, bridges, canals, dams, airports, sewerage systems, pipelines, structural components of buildings, and railways.
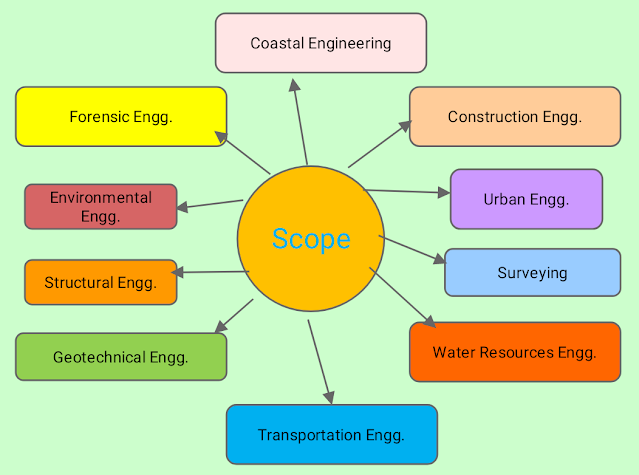
BRANCHES OF CIVIL ENGINEERING
Following are the branches of civil engineering :
1. STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING :
This discipline deals with :
- Analysis and design of concrete and steel structure.
- For e.g. multi-story buildings, bridges, towers, etc.
- Study of the durability and resistibility of such structures for live loads, wind and earthquake.
- Study of the properties of building materials according to the international specifications.
2. WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING :
This discipline includes :
- Basic concepts of water science and its related theorems and applications.
- Methods of transporting water from sources to distribution sites through channels and pipelines, water sources and storage system, types of dams and their design methods.
- Study of seawater movements and shore protection.
3. GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING :
Soil Engineering is an applied science dealing with the applications of principles of soil mechanics to practical problems. It has a much wider scope than soil mechanics, as it deals with all engineering problems related with soils.
It includes,
- Site investigations
- Design and construction of foundations
- Earth retaining structures
- Earth structures etc.
Geotechnical engineering is a broader term which includes soil engineering, rock mechanics and geology.
Rock mechanics is the science dealing with the mechanics of rocks.
Foundation engineering is a branch of civil engineering, which is associated with the design, construction, maintenance and renovation of footings, foundation walls, pile foundation, caissons and all other structural members which form the foundations of buildings and other engineering structures.
4. URBAN ENGINEERING :
This discipline deals with :
Designing
Constructing and
Maintaining the roads, water supply networks, sewers, municipal solid waste management and disposal, public parks, etc.
5. TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING :
This discipline involves
The planning
Design
Operation and
Maintenance of safe and efficient transportation systems.
Systems include roadways, railways, waterways, and intermodal operations.
6. COASTAL ENGINEERING :
This discipline deals with
- Specific demands posed by constructing at or near the coast, as well as the development of the coast itself.
- Protect costal areas against erosion and flooding.
7. FORENSIC ENGINEERING :
This discipline deals with :
The investigation of materials, products, structures or components that fail or do not operate or function as intended, causing personal injury, damage to property or economic loss.
To locate cause or causes of failure with a view to improve performance or life of a component, or to assist a court in determining the facts of an accident.
8. ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING :
This discipline deals with
Treatment of chemical, biological, or thermal wastes.
Purification of water and air.
Remediation of contaminated sites after waste disposal or accidental contamination.
9. SURVEYING :
Surveying is the branch of civil engineering.
It is the art and science of determining the relative position of various points or stations on, above or beneath the surface of the earth by measuring the horizontal and vertical distances, angles and using the details of these points to prepare a map or plan to any suitable scale.
10. CONSTRUCTION ENGINEERING :
This discipline deals with
- Planning and execution
- Transportation of materials
- Site development based on hydraulic,environmental, structural and geotechnical engineering.